How to Make Your Own Cattle Feed Pellets Step by Step
Feed makes up about 65% of the total cost in cattle farming, making it the largest expense. To save money and improve efficiency, more farmers are choosing to make their own cattle feed pellets.
Compared to roughage, pellet feed is more nutrient-dense and better balanced, helping cattle absorb nutrients more effectively. Its uniform size reduces feed waste by discouraging picky eating. Plus, the heat used during pelleting kills bacteria and helps lower the risk of disease.

Raw Material Preparation
Pellet-making starts with picking and prepping the right raw materials. Each type of material adds different nutrients. Most raw materials fall into a few main groups:
| Category | Typical Raw Materials |
| Energy Feed | Corn, sorghum, wheat, barley, molasses, distillers' grains |
| Protein Feed | Soybean meal, cottonseed meal, rapeseed meal, sunflower meal, fishmeal, meat and bone meal |
| Roughage | Hay powder, silage corn, straw powder, grass powder, tofu dregs, distiller's grains |
| Mineral Additives | Salt, limestone, bone meal, dicalcium phosphate, baking soda, magnesium oxide |
| Vitamin Additives | Vitamin A, Vitamin D, Vitamin E, B-complex vitamins |
| Palatability Enhancers | Molasses, coconut meal, alfalfa, creeping plants grass powder |
| Functional Additives | Fattening agents, buffers, stomach conditioners, enzymes, probiotics |
A well-balanced feed mix can improve feed utilization and enhance cattle growth efficiency. Below are two feed formulations suitable for beef and dairy cattle:
- Beef Cattle Finishing Formula: Cornmeal47.5%, Bran5%, Cottonseed cake10%, Additives1%, Salt0.5%, Bone meal1%, Wheat straw or grass powder35%.
- Dry/Intermediate Lactating Dairy Cattle Formula: Corn powder10%, Sorghum7%, Soybean meal4.5%, Shell powder1.5%, Corn germ meal4%, Hay9%, Tofu dregs15%, Silage corn32%.

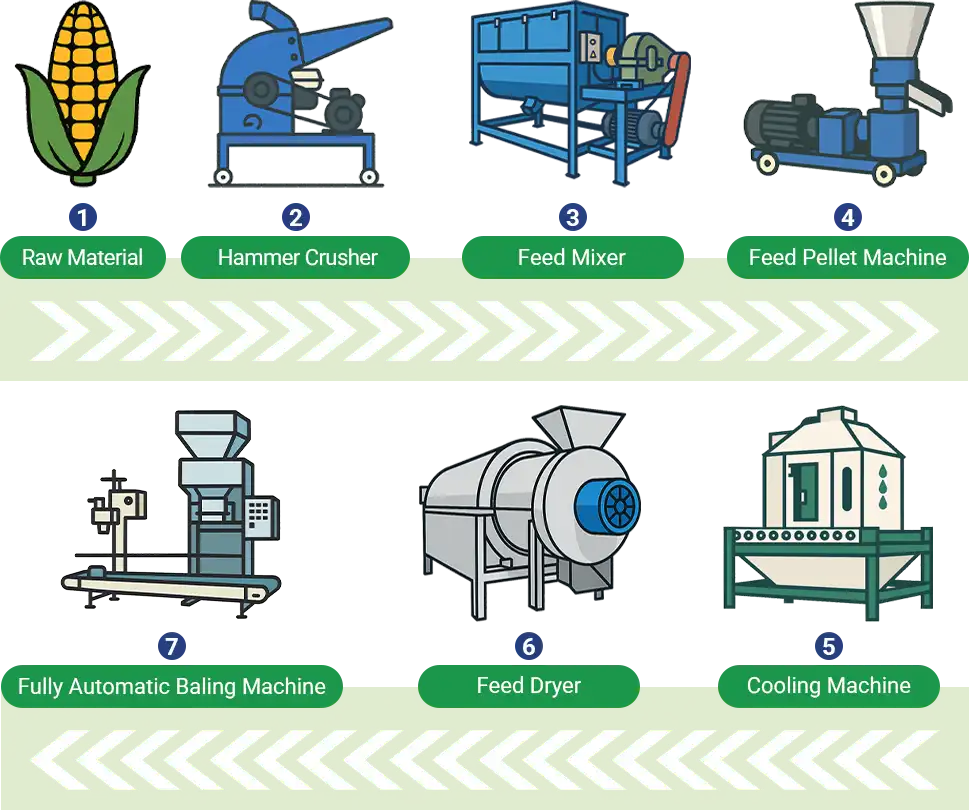
Making Cattle Feed Pellets: A 6-Step Process
Making cattle feed pellets typically involves the following 6 steps:
1.Raw Material Preprocessing
Prepare the raw materials as per the formula, and get rid of any dirt or metal. For whole roughage like hay or straw, cut it into 1-2 cm pieces. Grains like corn need to be crushed or flattened before grinding.
2.Grinding
Use a grinder to crush ingredients like corn, soybean meal, and wheat into fine particles, making them easier to mix and pellet. The particle size of the ground material should generally be less than 4mm. If it's too coarse, it will affect pellet formation; if it's too fine, the pellets may become too hard or produce too much dust.
3.Mixing
Mix the ground ingredients thoroughly, usually for 5-10 minutes. For large-scale production, a mixer is needed; for small-scale, manual mixing can be done, but it's important to ensure everything is evenly blended.
4.Pelletizing
Feed the mixed ingredients into the cattle feed making machine, where the mold and rollers compress them into cattle pellets. During pelleting, it's important to control the feed rate to ensure uniform pellet formation.
5.Cooling and Drying
Freshly made pellets have a high temperature and need to be cooled down properly. You can spread them out to cool naturally, or use cooling equipment to help lower the temperature and reduce moisture to below 14%, making them ready for packaging and storage.
6.Packaging and Storage
Pellets can be stored in bulk or in bags. The storage environment should be dry, moisture-free, and pest-proof. Since homemade pellets typically don't contain preservatives, it's best to use them as soon as possible. Be sure to check for any clumping or mold growth during storage.
Two Key Factors Affecting Pelletizing Quality
Although the process of making homemade cattle feed pellets is simple, achieving good pellet quality requires attention to two key factors. These are raw materials and equipment.
The Impact of Raw Materials on Pellet Formation
Generally, raw materials with high fiber content (such as alfalfa powder, beet pulp) have poor compressibility, making pellet formation more difficult. Starchy materials (like corn and barley) have good binding properties and are easier to compress into dense pellets.
Protein content also affects the pellet's toughness and palatability. It's important to balance high-protein, high-fiber ingredients with high-energy, low-fiber ones in the formula to maintain both nutritional value and pelletizing performance.
Below are the basic nutritional compositions of several common raw materials, which can be used as a reference when designing or adjusting feed formulas:
| Raw Material |
Crude Protein (%) |
Crude Fiber (%) |
TDN (%) |
Metabolizable Energy (MJ/kg) |
| Corn Grain | 8-9% | ~2-3% (NDF ~9.7%) | ~87-89% | ~13.0 MJ/kg |
| Barley Grain | ~11-13% | ~5% (NDF ~18%) | ~80-84% | ~12.0 MJ/kg |
| Wheat Bran | ~15-17% | ~10% | ~60-65% | ~9.0 MJ/kg |
| Soybean Meal | ~44-48% | ~6-7% | ~75-78% | ~11.5-12.5 MJ/kg |
| Cottonseed Meal | ~38-42% | ~12% | ~65-70% | ~10-11 MJ/kg |
| Corn Distillers' Grains | ~25-30% | ~8-10% | ~75-85% | ~12-13 MJ/kg |
| Alfalfa Hay Powder | ~16-18% | ~30% | ~50-55% | ~8-9 MJ/kg |
| Beet Pulp (Dry) | ~9-10% | ~20% | ~70-75% | ~11 MJ/kg |
If the pellets are easily breaking apart or difficult to form during pelleting, try reducing the proportion of high-fiber materials. You can also add a certain amount of starchy ingredients like corn or wheat bran to improve pellet formation.
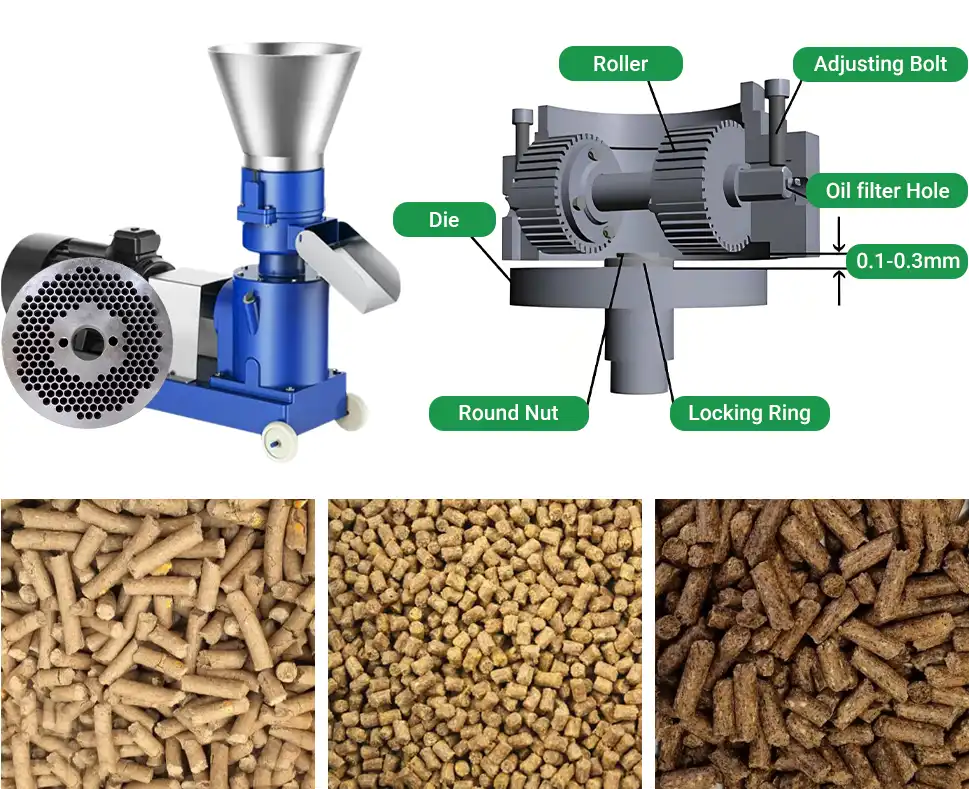
The Impact of Pellet Mills on Pellet Quality
The pellet mill is the core equipment in pellet production, and its inherent specifications have a significant impact on pellet quality. These specifications include:
- Die Compression Ratio: The compression ratio refers to the ratio of the effective length to the diameter of the die holes. It is a key factor affecting pellet density and durability. Formulas with more easily formed ingredients, like corn, are suitable for a high compression ratio. Materials with high fiber content and poor compressibility are better suited for a low compression ratio.
- Die Speed: The speed of the die affects the rate at which the material passes through the die holes and the compression time, which in turn influences pellet density. Small pellets are better suited for high speeds, while large pellets or low-density materials work better with lower speeds. When selecting equipment, ensure that the power is sufficient to match the raw material formula.
- Roller and Die Gap: The size of the gap between the rollers and the die affects the pellet's density. A smaller gap results in denser pellets, but if it's too small, it could damage the equipment. In practice, the gap can be adjusted to balance pellet hardness and smooth output.
Therefore, choosing a reliable pellet mill is especially important in actual production.

Kawise Pellet Mill: Making the Pelletizing Process More Efficient
The Kawise cattle feed pellet mill is designed with key structures tailored for optimal performance. It offers a range of die compression ratios, making it suitable for formulas with varying fiber content. The speed and die specifications match the common diameters of cattle feed pellets, ensuring stable pellet formation. The machine has a compact structure, making it easy to operate and maintain, ideal for everyday use.
Our pellet mills come in three power types: electric, diesel, and PTO, each suited for different environments and farming needs.
We have our own factory, and all equipment is sold directly at factory prices, offering better value for money. We also provide complete feed production lines and have many successful feed mill projects worldwide. For more information about our equipment, feel free to contact us anytime!

 Online Contact
Online Contact Send Message
Send Message
Need Some Help?
Contact us quickly and we will reply you within 24 hours. We will not disclose your information.