Pellet Mill Gear Drive Types and Performance Comparison
A pellet mill's power comes from its gear drive system. Different drive designs offer different torque levels, stability, and material handling ability. These structural differences shape how strong the machine runs and what materials it can process. Knowing them helps you pick the right model for your raw materials and target output.

Straight Bevel Gear Drive (Older Models)
Older small flat die pellet mills commonly used a straight bevel gear drive. This design is simple to produce, requires lower machining accuracy, and keeps manufacturing costs down. It worked well for early-generation machines and was suitable for light loads and intermittent pellet production.
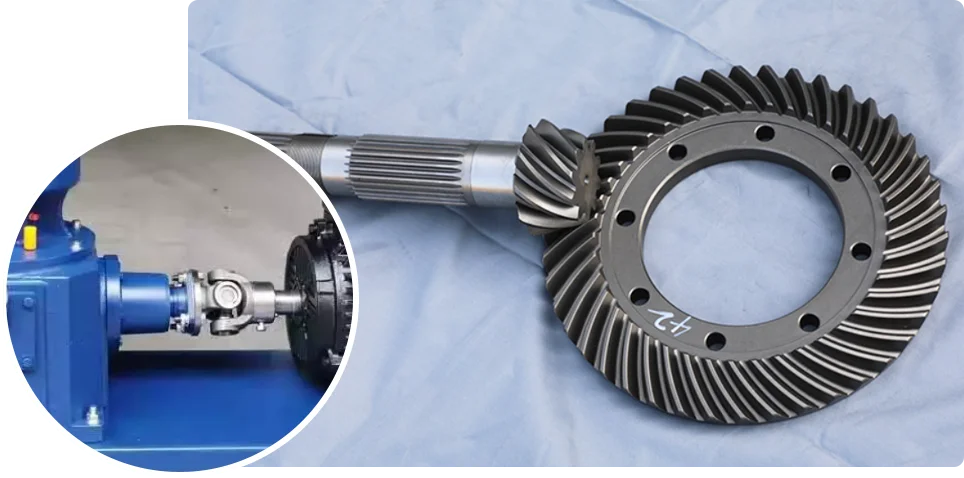

Power Transmission
Once the motor starts, the driving bevel gear meshes with the driven gear and redirects power to the main shaft. The shaft delivers steady torque to turn the rollers or die, creating the pressure needed to form pellets and keeping the machine running through each cycle.

However, the simple structure also brings clear limitations:
- Small gear contact area
- Limited torque output
- Larger backlash and noticeable noise
- Lower surface hardness, leading to faster wear under heavy load
- Short oil seal life and higher risk of leakage
- Single force point, which reduces overall load capacity
Suitable Materials
This drive structure works best with fine, easy forming feed ingredients, such as ground corn, wheat bran, soybean meal, and standard premix powders.
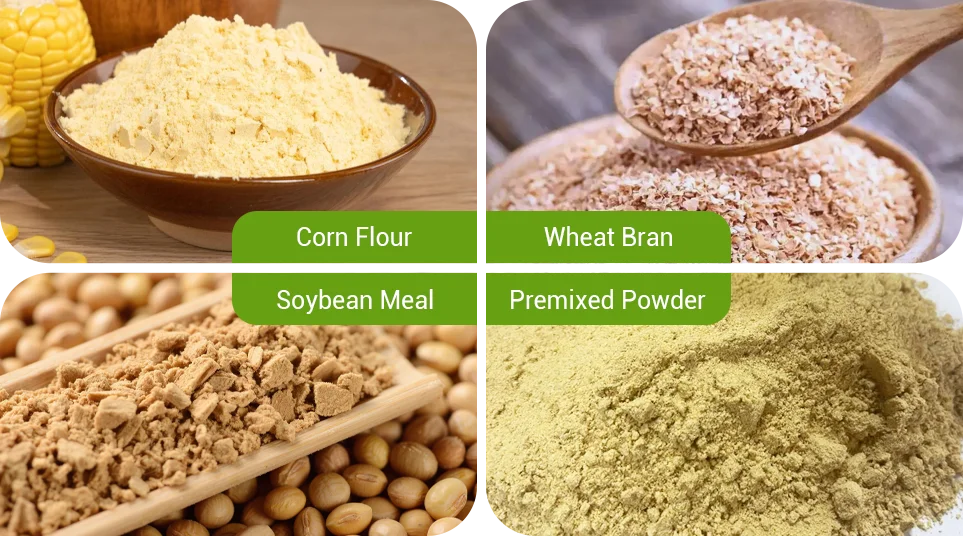
If the formula contains a high level of coarse fiber, such as grass powder, straw powder, or shell-based materials, or if the machine needs to run for long periods, the system may clog. This can lead to motor overload or gear damage.
Automotive Differential Gear Drive
As users began demanding higher output and longer continuous operation, pellet mill transmission systems also evolved.
Compared with older designs, the differential gear system used today delivers stronger torque, smoother operation, and much better durability.
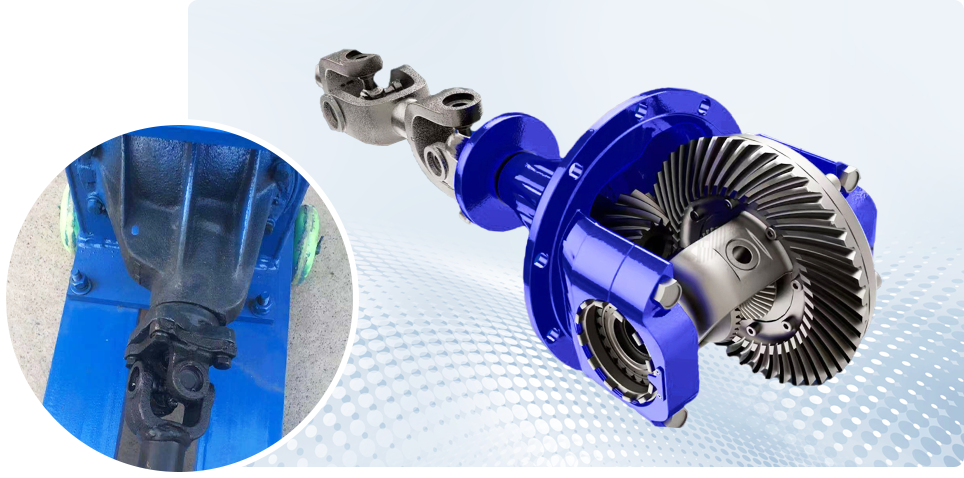

Power Transmission
The differential style gearbox provides strong torque reduction for the pellet mill. Power from the motor enters the gearbox, where the main bevel gear slows the speed and increases torque. The locked planetary gears let the unit work as a heavy duty reducer that drives the main shaft.
With low speed and high torque, the shaft turns the rollers and maintains the pressure needed to form pellets.
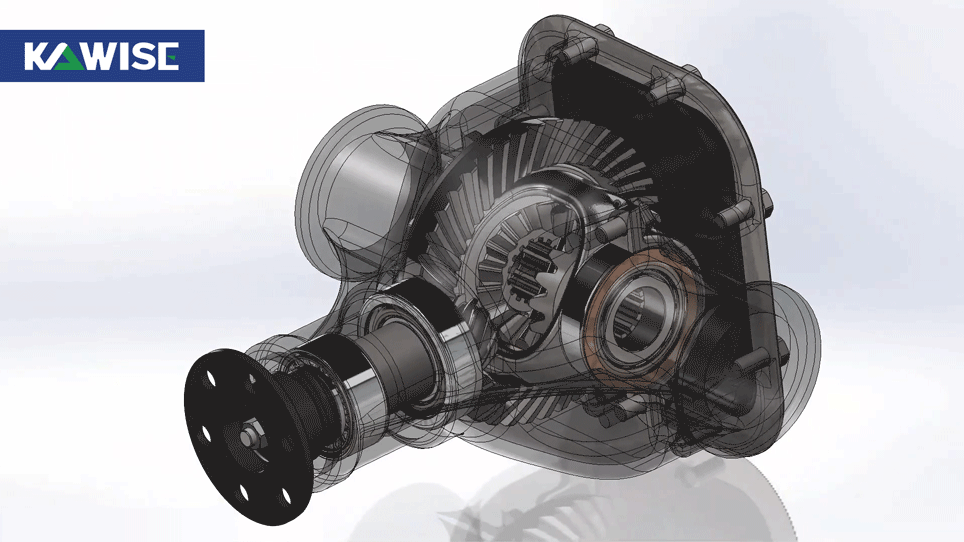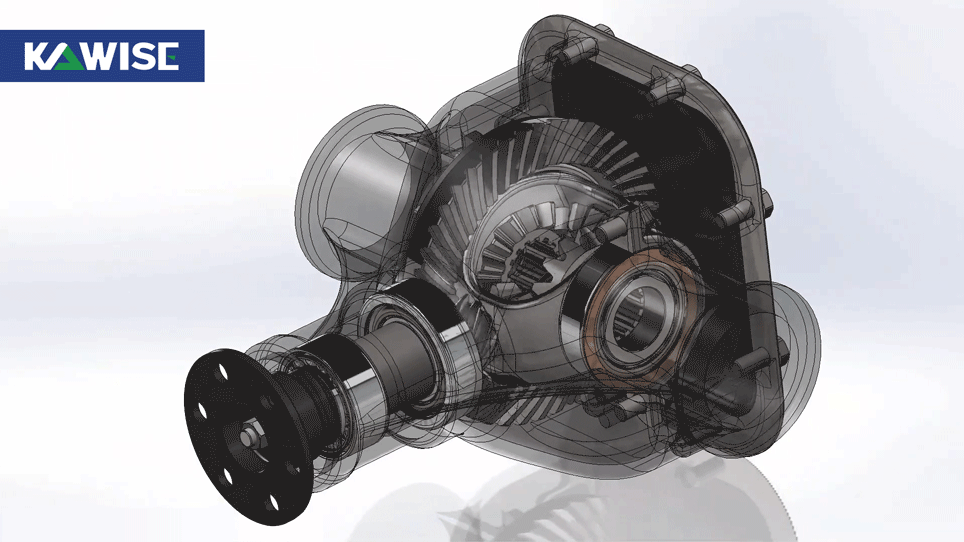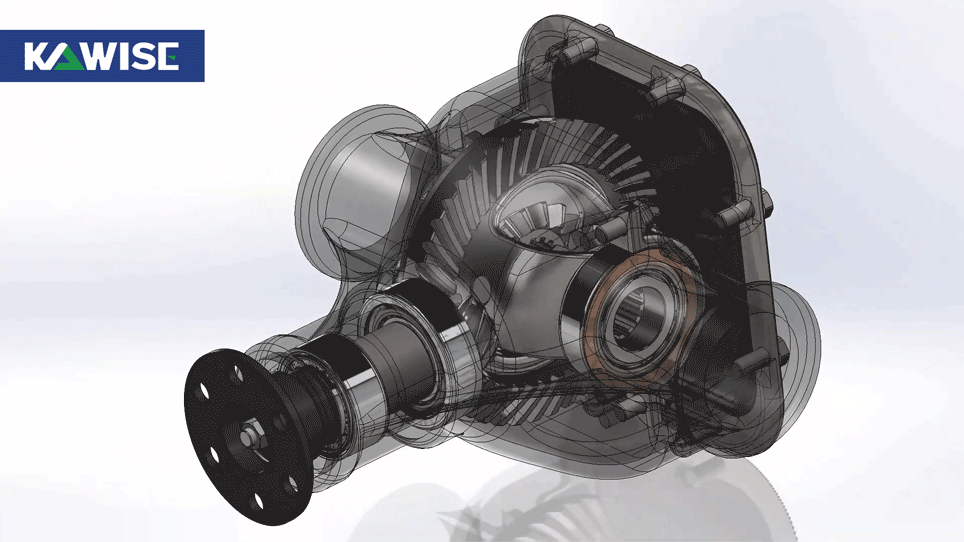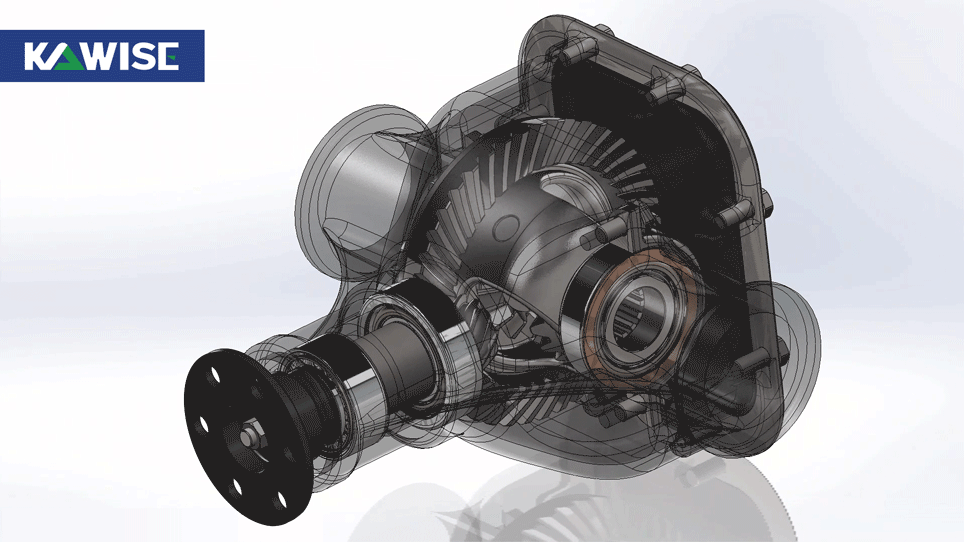
Suitable Materials
Differential drives use spiral bevel or offset gears with line contact, giving higher and more stable torque. This helps the rollers handle high compression ratios and high fiber materials with smoother, quieter operation.
Suitable materials include:
- Corn meal, wheat bran, rice bran
- Soybean meal and rapeseed meal
- Standard poultry and livestock diets
- Feed bases with moderate oil content
- High fiber forage materials (for roller rotating models)

Not Suitable for This Machine
✗ Biomass materials like wood chips, bark, bamboo powder, straw pieces, and rice husk
✗ Hard or high silica materials
✗ Biomass fuel or industrial formulations
These materials need much higher compression and create heavy resistance, which can overload the main shaft, rollers, and gears. Long term use under these conditions may cause rapid wear or machine shutdown.
Heavy Duty Gearbox Structure
This gearbox is built for high compression, long continuous runs, and tough materials like wood chips and straw. It provides strong power and stable torque and is commonly used in flat die biomass pellet mills and ring die pellet mills for heavy duty operation.
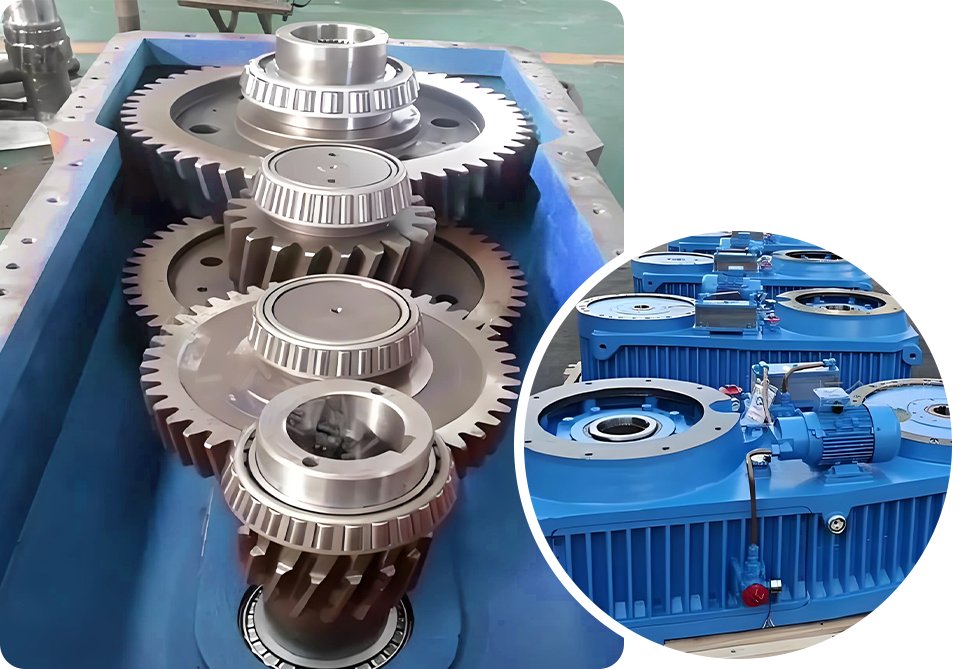
Structural Features
The gearbox uses hardened helical gears in multiple stages to slow the speed and increase torque. The large contact area keeps transmission stable under high compression.
Large module gears and heavy duty bearings raise load capacity and keep the main shaft rigid. Oil bath or independent lubrication cools and protects the gears, ensuring reliable performance even under heavy load.

Suitable Materials
The higher torque and stable transmission allow this system to handle both regular feed ingredients and tough biomass materials like wood chips, straw, and rice husk. Ring die pellet mills keep steady pressure even under continuous load.

Application Scenarios
The higher torque and stable transmission let the pellet mill maintain reliable pressing during long continuous runs. This makes the system suitable for biomass fuel production, feed supply for medium and large farms, and factories that operate for extended hours.
For operations that require consistent output and long term stability, this drive system provides a stronger and more dependable performance.

Performance Comparison of 3 Drive Systems
| Item | Straight Bevel Gear | Automotive Differential | Heavy Duty Gearbox |
| Common Models | Old flat die | Flat die feed mills | Flat die / ring die biomass |
| Cost | Low | Medium | High |
| Torque | Low | Medium | High |
| Material Fit | Fine feed powders | Regular feed | Wood, straw, husk |
| Continuous Run | Weak | Moderate | Strong |
| Output | Low | Medium | High, scalable |
| Durability | Fast wear | Stable | Industrial grade |
| Noise | High | Medium | Low |
Different drive systems give flat die and ring die pellet mills clear differences in power output and material handling.
Choosing the right structure based on raw materials, target capacity, and operating time helps achieve higher efficiency and more reliable pelletizing performance in actual production.

 Online Contact
Online Contact Send Message
Send Message
Need Some Help?
Contact us quickly and we will reply you within 24 hours. We will not disclose your information.