Setting Up a Fish Feed Line in India: What You Need to Know
India is the third-largest aquaculture producer globally, with steady growth in freshwater fish production, including catfish, tilapia, and rohu. As aquaculture expands, the demand for fish feed, especially floating and sinking pellets, is rapidly increasing. In this context, we'll explore the feasibility of setting up a fish feed production line in India, focusing on market demand, raw material supply, and policy support.

Market Potential and Demand
India's fish feed market has seen strong growth in recent years. According to market research, the aquaculture market in India will reach $1.6 billion by 2024, with projections to grow to $3.1 billion by 2031, driven by a CAGR of 10.4% from 2025 to 2031. This growth is directly fueling the steady rise in demand for commercial fish feed.
Currently, freshwater fish like carp, tilapia, and catfish dominate Indian aquaculture, with increasing production of high-value species like shrimp and basa fish in some areas(Fish Feed Industry In India Size & Share Analysis). As farming density grows and feeding practices evolve, more farmers are adopting standardized, nutritionally balanced pellet feed. By 2024, India's annual fish feed consumption is expected to reach 1.9 million tons, with a projected CAGR of 8.13% from 2025 to 2033.
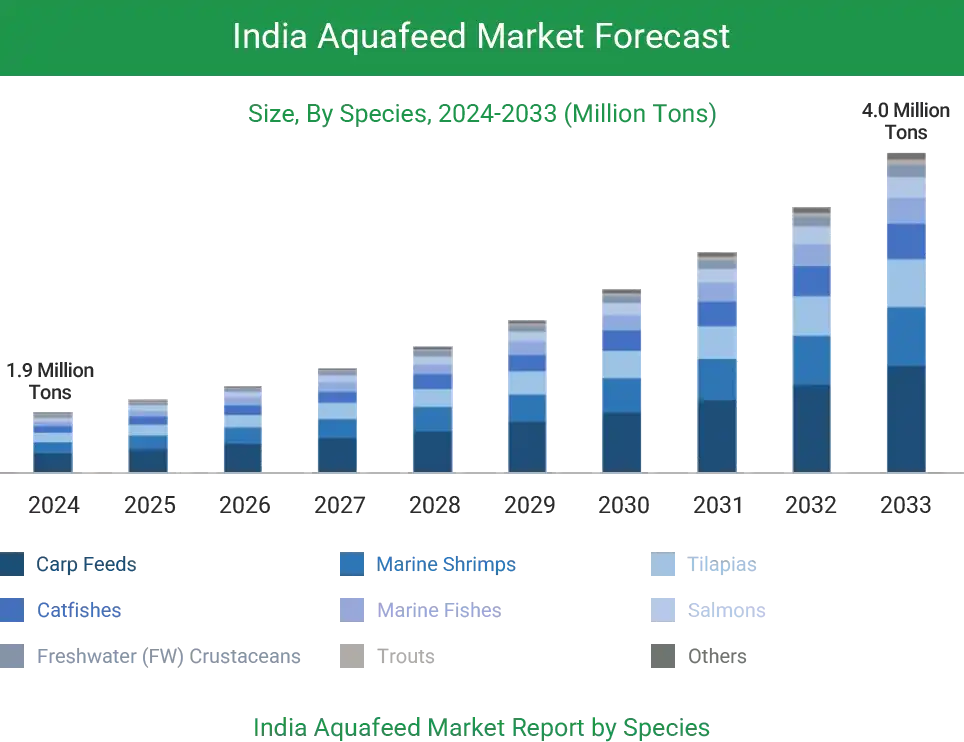
The use of floating and sinking pellets is steadily increasing, gradually replacing the earlier common use of homemade powder and wet feed. In aquaculture-intensive regions like Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Odisha, and West Bengal, commercial pellet feed has become the dominant choice.
Industry estimates show that fish feed makes up the majority of the aquaculture feed market, with over 65% of the share focused on freshwater fish formulations. The demand for floating pellets is growing, and feed products are quickly adapting to different fish ages and farming methods. Overall, India's market is increasingly favoring efficient, easy-to-use, and cost-effective pellet feeds, driving the growth of local production lines.

Policy Support
The Indian government provides clear and ongoing policy support for the aquaculture and feed industries. Programs like the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY) and the Fisheries Infrastructure Development Fund (FIDF) offer financial support and subsidies for new feed mills and raw material processing centers, significantly reducing initial investment costs. Several state governments, such as Andhra Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh, also offer incentives like land, electricity, and logistics subsidies to encourage businesses to set up production facilities.

India has recently lowered import duties on key ingredients like fishmeal, shrimp shell powder, and insect protein, helping businesses adopt more efficient formulas and advanced technologies, while offering more room for production upgrades and cost control.
Local Raw Material Supply Advantage
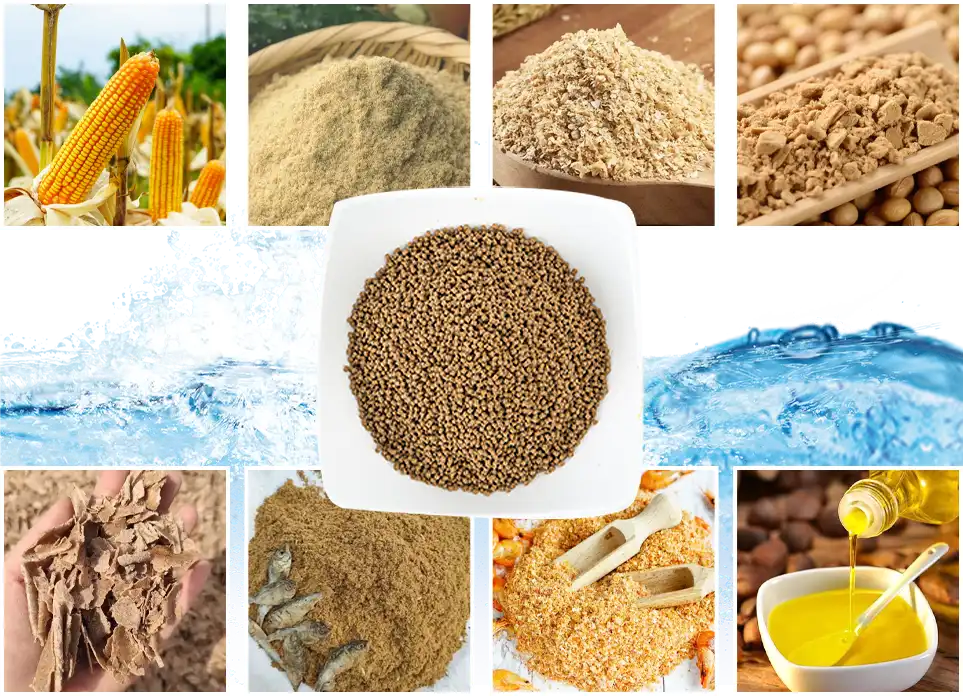
Key ingredients for fish feed, such as corn, rice bran, soybean meal, peanut meal, and fishmeal, are used in different feed types (floating or sinking), with similar base ingredients. The availability and cost of these raw materials are crucial factors in choosing a factory location and ensuring long-term operation.
India has a clear advantage in this area, with its strong agricultural base and abundant fisheries resources. Fish feed ingredients are widely available across several states, allowing for local sourcing.
Fish Feed Ingredients and Production Regions
| Type | Main Ingredients | Key Regions |
| Energy | Corn, Rice Bran, Wheat Bran | Maharashtra, Punjab, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh |
| Plant Protein | Soybean Meal, Peanut Meal, Cottonseed Meal | Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, Telangana, Tamil Nadu |
| Animal Protein | Fishmeal, Shrimp Shell Powder | Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Coastal Areas |
| Oils & Additives | Vegetable Oil, Lysine | Available Nationwide |
Data Base:USDA Foreign Agriculture Service
The biggest advantage of local raw material supply is lower cost, faster access, and reduced risk. For example, soybean meal and rice bran are widely available in many states and are key ingredients in both floating and sinking pellets. Compared to imported fishmeal, using locally sourced plant proteins not only offers cost advantages but also ensures a more stable supply and easier formula adjustments.

Flexible Process and Equipment
After evaluating market potential, raw material availability, and policy support, the next step is configuring the production line and capacity. The design should balance palatability, nutritional stability, and processing efficiency based on fish feed formulations and pellet requirements. Below, we outline typical production processes for both floating and sinking fish feed.
Production Line Process
For users planning to set up a fish feed pellet plant in India, a clear production line design is crucial. It not only impacts equipment selection but also directly affects capacity, quality control, and cost efficiency.
A standard fish feed pellet production line typically includes the following processes:

Floating vs. Sinking Feed Processing
Floating and sinking feeds are produced differently.
Sinking feed is made using a pellet mill, creating denser pellets that sink, ideal for bottom-feeding fish like catfish and basa. Equipment should be selected based on the target fish species.
Floating feed is typically produced with an extruder, which uses heat and pressure to create air pockets in the pellets, allowing them to float. This is best for surface-feeding fish like tilapia and carp. While extruders are mainly used for floating feed, they can also be adjusted for sinking feed production.

To find out which feed is best for your fish, here's a detailed guide:
Floating or Sinking Feed: What's Best for Your Fish?
Capacity and Equipment Recommendations
The configuration of a fish feed pellet production line can be adjusted to suit specific needs. When setting up a plant, it's important to customize the setup based on the fish species, feed type, capacity, and budget. Here are three options for different scales and investment levels to help with your planning.
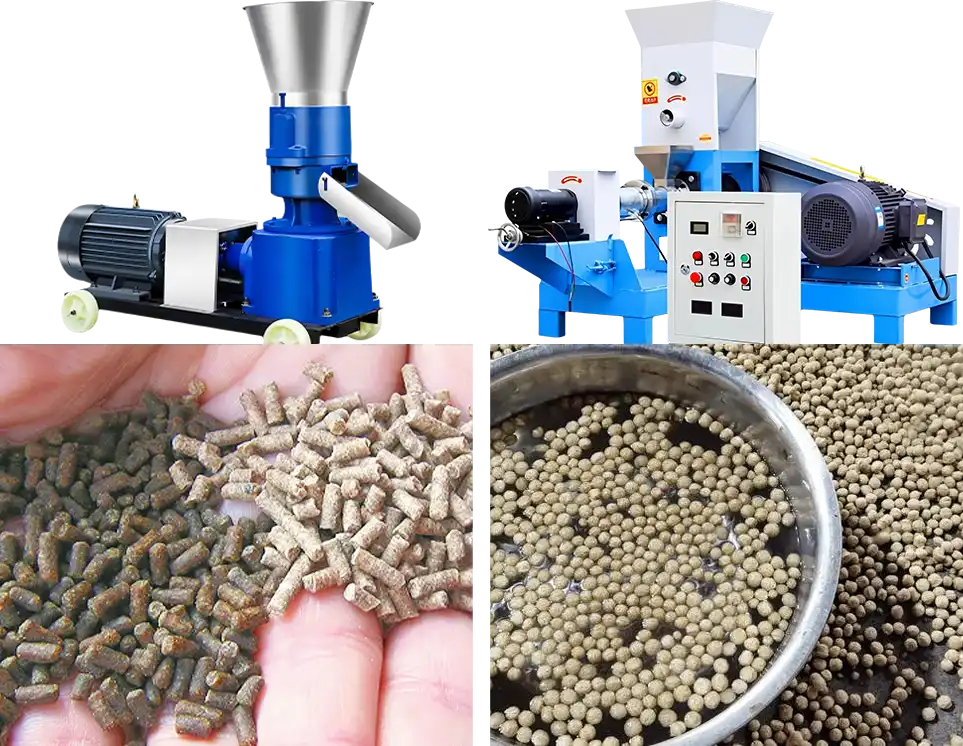
Economy Sinking Fish Feed Production Line (80-500 kg/h)
This economy solution is perfect for small farms, farmers, or beginners, designed for sinking feed production. It's space-efficient, low-cost, and easy to operate, ideal for those on a budget or testing small-scale production of stable sinking fish feed.
Recommended Equipment
- Small Hammer mill
- Small feed mixer
- Flat die feed pellet machine (for sinking feed only)
- Cooler or natural cooling
- Manual packing or basic sealing machine (optional)
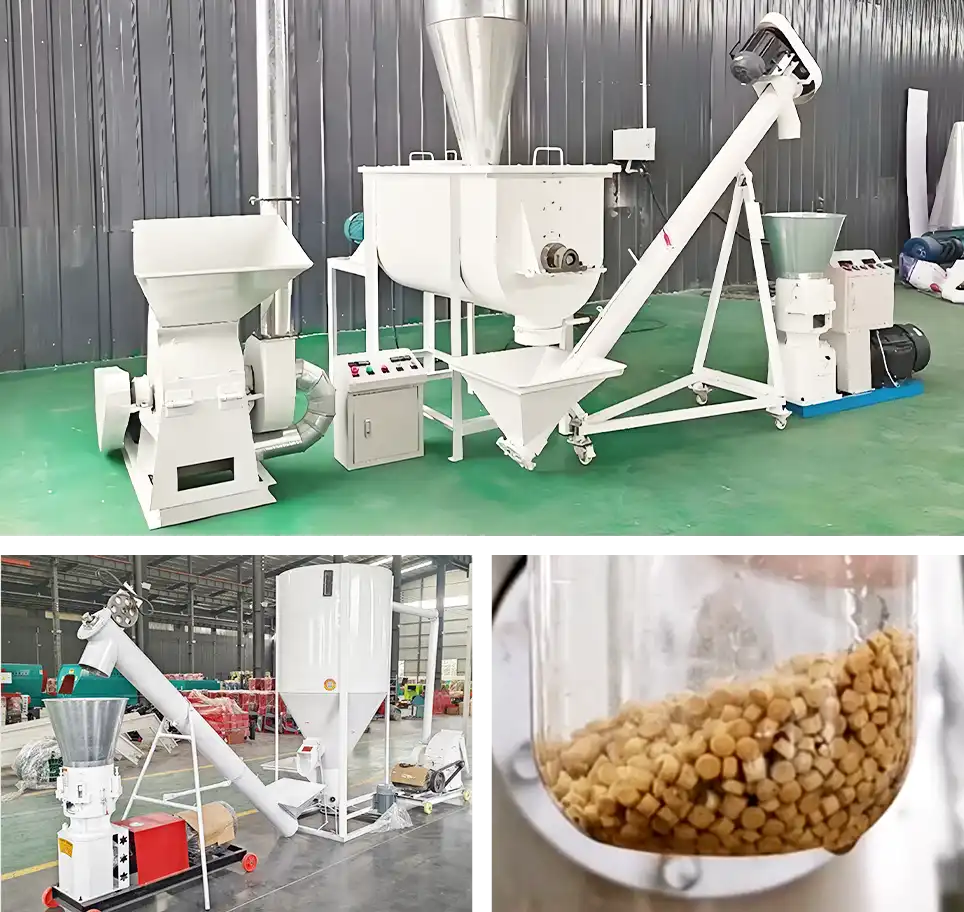

Standard Floating Fish Feed Production Line (50-400 kg/h)
This solution offers better efficiency, feed quality, and process optimization than the economy option, making it perfect for floating feed production. It's ideal for medium and small farms or feed mills focused on quality and stable output, meeting higher production demands while offering good value.
- Hammer Mill (manual feeding required)
- Horizontal Mixer
- Steam Boiler + Conditioner
- Single-Screw Extruder
- Small Drum/Spray Coating Machine
- Counterflow Cooler + Screener
- Small Storage Bin
- Quantitative Weighing and Packing Machine
*The feed extrusion process uses heat, pressure, and steam, which takes time to expand and cool the materials, resulting in slower production and lower output.
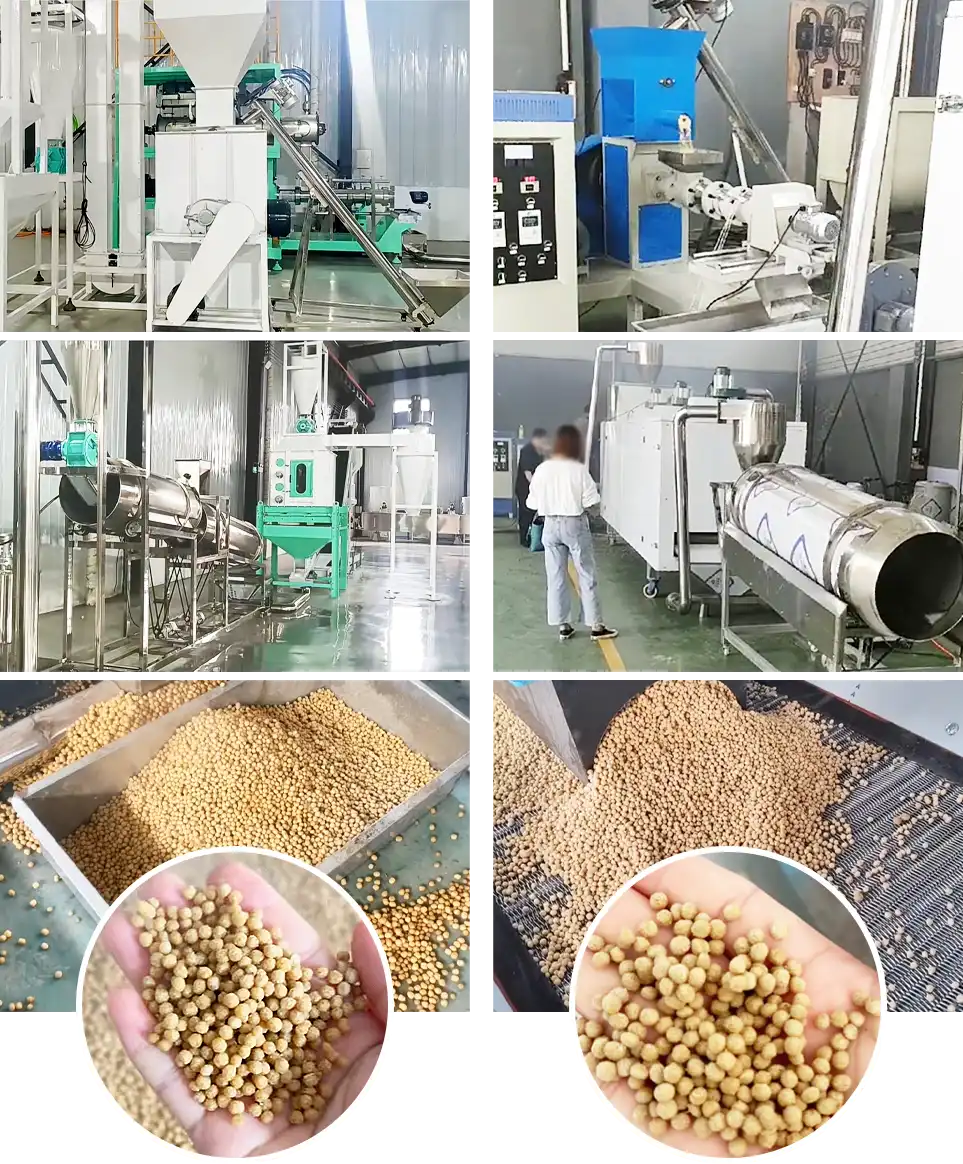

Fully Automated High-Capacity Configuration (1-2 T/h)
This solution is perfect for large feed mills, processing plants, or export-focused businesses, designed for high-volume, high-frequency production. With higher automation, faster efficiency, and smoother processes, it handles large orders and continuous supply better. It supports both sinking and floating feed production for various fish species.
- Automatic Raw Material Feeding System (Screw Conveyor + Storage Bin)
- High-Capacity Hammer Mill
- Dual-Axis High-Efficiency Mixer
- Conditioner + Steam Boiler
- Twin-Screw Extruder
- Steam Oven
- Buffer Bin
- Coating/Drum Spray Coating Machine (for Oils/Vitamins/Additives)
- Counterflow Cooler and Sifter
- Material Conveying System
- Fully Automated Packaging Machine
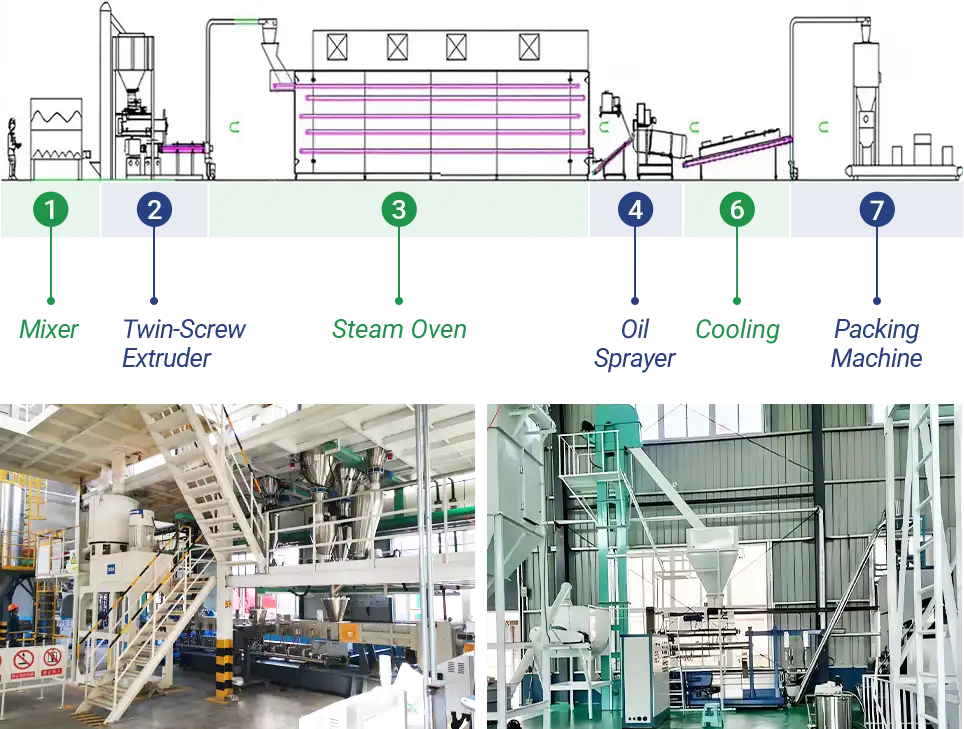
*All the configurations above are for reference only. The equipment can be customized based on specific capacity and production needs.
India's fish feed market is stable, with ample raw materials and supportive policies, making it an ideal location for production lines. Whether you're starting small or expanding, production lines can be customized to balance cost and efficiency for high-quality results.
Contact us for tailored design and equipment recommendations for your fish feed production line.
 Online Contact
Online Contact Send Message
Send Message
Need Some Help?
Contact us quickly and we will reply you within 24 hours. We will not disclose your information.